Discovery of Novel P1 Groups for Coagulation Factor VIIa Inhibition Using Fragment-Based Screening.
Cheney, D.L., Bozarth, J.M., Metzler, W.J., Morin, P.E., Mueller, L., Newitt, J.A., Nirschl, A.H., Rendina, A.R., Tamura, J.K., Wei, A., Wen, X., Wurtz, N.R., Seiffert, D.A., Wexler, R.R., Priestley, E.S.(2015) J Med Chem 58: 2799-2808
- PubMed: 25764119
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jm501982k
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4X8S, 4X8T, 4X8U, 4X8V - PubMed Abstract:
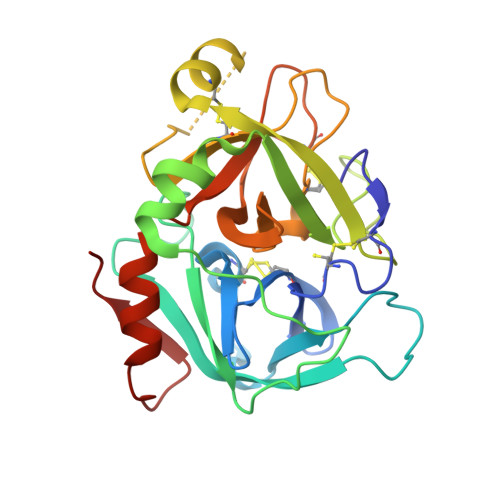
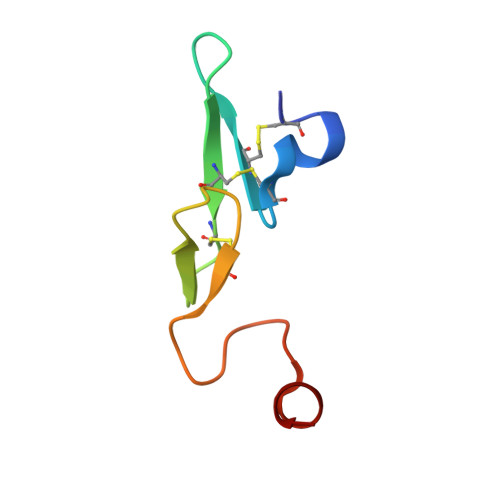
A multidisciplinary, fragment-based screening approach involving protein ensemble docking and biochemical and NMR assays is described. This approach led to the discovery of several structurally diverse, neutral surrogates for cationic factor VIIa P1 groups, which are generally associated with poor pharmacokinetic (PK) properties. Among the novel factor VIIa inhibitory fragments identified were aryl halides, lactams, and heterocycles. Crystallographic structures for several bound fragments were obtained, leading to the successful design of a potent factor VIIa inhibitor with a neutral lactam P1 and improved permeability.
Organizational Affiliation:
†Bristol-Myers Squibb Co., Research and Development, 311 Pennington-Rocky Hill Road, Pennington, New Jersey 08543, United States.